 Malaysian Government & Politics
Malaysian Government & Politics
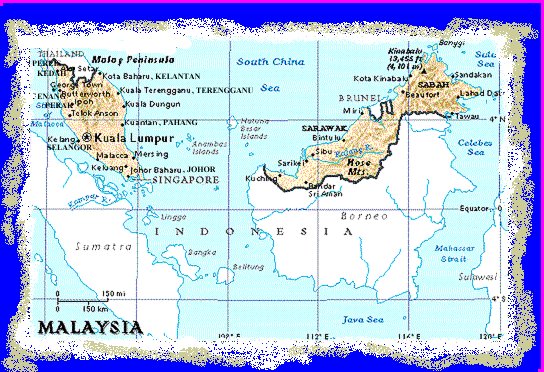
Map of Malaysia
MALAYSIA - Retrospective
Straddling the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea, Malaysia has always been a melting pot of cultures, as traders from
the West meet those from the East. The population comprises the Malays, Chinese and Insians with smaller group of indigenous
peoples Orang Asli, Eurasian and Indonesians. Since 1957, when the independence movement resulted in the Federation of
Malaya, followed by the formation of Malaysia in 1963, the country has forged ahead as a successful developing country. The
turbulent history, leading up to modern Malaysia's rapid development, illustrates some of the elements, which shaped the
country's destiny.
|
|
MALAYSIA - States
Malaysia has 13 states and 2 federal territories
Wilayah Persekutuan / Federal Territories : Kuala Lumpur and Labuan
States : These nine states have hereditary rulers known as the Sultan and Yam Tuan Besar for Negeri Sembilan.
From these states, Perlis, Kedah, Perak, Selangor, Negeri Sembilan, Johor, Pahang, Terengganu and Kelantan, the Head of
State of Malaysia, The King or Yang Di-Pertuan Agung, is elected every five years. The nine states have hereditary rulers known
as Sultan and Yam Tuan Besar for Negeri Sembilan.
For Penang, Melaka, Sabah and Sarawak, the Governor is Head of State.
MALAYSIA - Parliament
The Government is parliamentary democracy based upon universal suffrage. The executive power is vested in the head of
Government, the Prime Minister, who presides over the Cabinet, comprising the Government Ministers.
Parliamentary comprises two houses; The Dewan Rakyat, which is fully elected, and the Dewan Negara (Senate) to which
members are nominated by the Agung (King). Senate members are citizens who have given distinguished public service, have
distinguished professional careers, or who represent interests of racial minorities and aboriginal people.
MALAYSIA - State Governments
Menteri Besar (Head of Local State Governments) are elected to office, together with a Dewan Negeri or State Assembly. For
the states of Penang, Melaka, Sabah and Sarawak, Ketua Menteri or Chief Minister is the Local State Government Head.
The supreme law of the nation is a written federal constitution, which can only be amended by a two-thirds majority in
Parliament.
 Government Ministries Government Ministries
 Prime Ministers Department Prime Ministers Department
 Ministry of Youth and Sports Ministry of Youth and Sports
 Ministry of Finance Ministry of Finance
 Ministry of Domestic Trade & Consumer Affairs Ministry of Domestic Trade & Consumer Affairs
 Ministry of Energy,Telecommunication & Posts Ministry of Energy,Telecommunication & Posts
 Ministry of Primary Industries Ministry of Primary Industries
 Ministry of Transport Ministry of Transport
 Ministry of Science, Technology and The Environment Ministry of Science, Technology and The Environment
 Ministry of Information Ministry of Information
 Ministry of Entrepreneur Development Ministry of Entrepreneur Development
 Ministry of Education Ministry of Education
 Ministry of International Trade & Industry Ministry of International Trade & Industry
 Ministry of Human Resources Ministry of Human Resources
 Ministry of Tourism Ministry of Tourism
 Ministry of Agriculture Ministry of Agriculture
 Political Parties Political Parties
 UMNO UMNO
 UMNO Youth UMNO Youth
 Opposition Party-DAP Opposition Party-DAP
 State Governments State Governments
 Perlis Indera Kayangan Perlis Indera Kayangan
 Kedah Darulaman Kedah Darulaman
 Kelantan Darul Naim Kelantan Darul Naim
 Terengganu Darul Iman Terengganu Darul Iman
 Pulau Pinang(Penang) Pulau Pinang(Penang)
 Perak Darul Ridzuan Perak Darul Ridzuan
 Selangor Darul Ehsan Selangor Darul Ehsan
 Pahang Darul Makmur Pahang Darul Makmur
 Negeri Sembilan Darul Khusus Negeri Sembilan Darul Khusus
 Melaka (Malacca) Melaka (Malacca)
 Johor Darul Takzim Johor Darul Takzim
 Sabah Sabah
 Sarawak Sarawak
 Government Agencies Government Agencies
 Department of Environment (DOE) Department of Environment (DOE)
 Road Transport Department (JPJ) Road Transport Department (JPJ)
 Public Works Department (JKR) Public Works Department (JKR)
 National Archives of Malaysia (Arkib Negara) National Archives of Malaysia (Arkib Negara)
 National Library of Malaysia (PNM) National Library of Malaysia (PNM)
 Forest Research Institute (FRIM) Forest Research Institute (FRIM)
 Immigration Department of Malaysia Immigration Department of Malaysia
 Malaysia Agriculture Research & Development Institute (MARDI) Malaysia Agriculture Research & Development Institute (MARDI)
 Palm Oil Registration & Licensing Authority (PORLA) Palm Oil Registration & Licensing Authority (PORLA)
 Palm Oil Research Institute of Malaysia (PORIM) Palm Oil Research Institute of Malaysia (PORIM)
 SIRIM SIRIM
 Tenaga Nasional Berhad Tenaga Nasional Berhad
 Telekom Malaysia Berhad Telekom Malaysia Berhad
 Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia
 Bank Negara Malaysia Bank Negara Malaysia
 Royal Customs & Excise Department of Malaysia Royal Customs & Excise Department of Malaysia
 MIMOS MIMOS
 Technology Park Malaysia Technology Park Malaysia
 Fire & Rescue Departmentn Fire & Rescue Departmentn
 Department of Survey & Mapping of Malaysia Department of Survey & Mapping of Malaysia
 Malaysia Industrial Development Authority Malaysia Industrial Development Authority
 Department of Co-operative Development Malaysia Department of Co-operative Development Malaysia
 Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka
|
 Malaysia Government
Prime Minister's Home Page
Parliament of Malaysia
Government Ministries
State Governments
Government Agencies
Political Parties
Lighter Side of Malaysia
Guestbook
Voice Mail
Search
Malaysia Government
Prime Minister's Home Page
Parliament of Malaysia
Government Ministries
State Governments
Government Agencies
Political Parties
Lighter Side of Malaysia
Guestbook
Voice Mail
Search




